Skaffold
From the Skaffold site:
Skaffold is a command line tool that facilitates continuous development for Kubernetes-native applications. Skaffold handles the workflow for building, pushing, and deploying your application, and provides building blocks for creating CI/CD pipelines. This enables you to focus on iterating on your application locally while Skaffold continuously deploys to your local or remote Kubernetes cluster.
Skaffold can use different types of Kubernetes sources like plain manifest YAML files, Kustomize overlays, and Helm charts. Our convention is to use Kustomize to define overlays relevant for each type of usage and execution environment, as discussed here.
Skaffold also allows different tools to execute the build of the application and container image, including Dockerfile and
Jib + Maven or Gradle. Our convention is to use the Jib Maven build configuration, which is enabled by including the
jib-maven-plugin-tile in the project’s pom.xml tiles-maven-plugin configuration.
skaffold.yaml is the configuration file for Skaffold and is placed at the root of the project. Like most
To initialize the project skaffold.yaml and supporting scripts from the standard
NGSS
template, follow the instructions in the
migration guide.
|
Here are some example configurations for skaffold.yaml and the plugin configuration in the service module pom.xml.
apiVersion: skaffold/v4beta6
kind: Config
.commonVariables:
- &sandboxBaseImage dtr.mapsandbox.net/base/java21-jre:1.3.0
- &productionBaseImage utility.apps.va.gov/base/java21-jre:1.3.0
- &localDevBaseImage gcr.io/distroless/java21-debian12:debug
metadata:
name: my-service
build:
artifacts:
- image: dtr.mapsandbox.net/ckm/my-service (1)
context: .
jib:
project: my-service (2)
# type: maven (default) (3)
args:
- -Pskaffold-dev # ngss-maven-tiles-based profiles
fromImage: *localDevBaseImage # lightweight image for development
sync:
auto: true # enables hot reloading of application without full re-build/re-deploy
manifests:
hooks:
before:
- host:
command: [ "bash", "-c", "./localize.sh"] # fetch dependent Kustomize resources when changed
kustomize:
paths:
- kubernetes/localized/dev-with-dependencies/dev-with-dependencies # use "localized" dependencies (4)
profiles: (5)
- name: localize # Forces 'kustomize localize' to run during build, regardless of changes made to Kustomize files
# ...
- name: debug-all # Adds Java debug options to every deployment, to allow setting breakpoints in dependency code
# ...
- name: integration # Used in 'scripts/start-skaffold.sh' when the Maven 'with-skaffold' profile is activated
# ...
- name: post-sync-test # Automatically execute tests after re-syncing/re-deploying the changes made in source
# ...
- name: sandbox-build-test # Used in Jenkins CI Sandbox environment
# ...
- name: staging-build-test # Used in Jenkins CI Staging/SQA environment
# ...
- name: map-sandbox-deploy # Used for deploying to Sandbox environment
# ...
- name: map-staging-deploy # Used for deploying to Staging/SQA environment
# ...
- name: map-prod-deploy # Used for deploying to Prod environment
# ...| 1 | The result container image name to build and push after building the application |
| 2 | The relative directory of the Maven module to be built |
| 3 | The type of build to use with the jib tool (in this case, it maps to jib-maven-plugin) |
| 4 | The relative path to the Kustomize overlay to be deployed after building the container image |
| 5 | Explained in more detail below |
<project>
<properties>
<ngss-maven-tiles.version>{latest-tiles-version}</jib-maven-plugin-tile.version>
</properties>
<!-- ... -->
<build>
<!-- ... -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>io.repaint.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tiles-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${tiles-maven-plugin.version}</version>
<extensions>true</extensions>
<configuration>
<tiles>
<tile>gov.va.mobile.tools.maven:jib-maven-plugin-tile:${ngss-maven-tiles.version}</tile>
<!-- other tiles -->
</tiles>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Running
In the normal development workflow, the main command executed is skaffold dev,
which watches for file changes in the service module directory and rebuilds and redploys automatically when it discovers
a change.This behavior is highly configurable and is described fully in https://skaffold.dev/docs/references/cli/.
When a change is detected, the Maven build is run and a new image is produced as a result.This image is referenced
in the Kuberenetes deployment that is rendered from the Kustomize path set in the kustomize configuration.
skaffold.yaml profiles
- default
-
The default (first) profile, defined without a "profile" designation, specifies how to build and test locally
localize-
Forces the Kustomize "localization" of all Kustomize overlays, which resolves and fetches all Git references, like to other dependent service Kustomizations, regardless of whether any files in the source Kubernetes directory have changed.
|
Think of the See Localize For more info. |
debug-all-
Applies patches to every dependency deployment that enable remote Java debugging, so that the developer can set breakpoints in any Java service’s source code
integration-
Activated in the
start-skaffold.shscript which is called with the Mavenwith-skaffoldprofile. sandbox-build-test-
Defines how to build and test the service in Jenkins Sandbox
staging-build-test-
Defines how to build and test the service in Jenkins SQA
map-sandbox-deploy-
Defines the profile for a service deployment to a namespace in Sandbox
map-staging-deploy-
Defines the profile for a service deployment to the namespace
sqain SQA map-prod-deploy-
Defines the profile for a service deployment to the namespace
prodin Production
Common commands for developing using Skaffold
-
skaffold dev-
Used for active development of features
-
Automatically port-forwards service ports specified in
skaffold.yaml -
The Cloud Code plugin’s main run configuration (if enabled) defaults to this subcommand
-
By default, this command will monitor the files (e.g. java source/classes) that define your container.
-
When files change that impact your container, it will hot reload your deployment automatically
-
If you run
mvn clean verifyduring askaffold dev, it will cause the container to reload and could cause tests to fail. Useskaffold run --port-forwardfor executingmvn clean verify
-
-
skaffold run --port-forward-
Used for finalizing development and running tests
-
Using the
--port-forwardflag, the skaffold will standup your deployment and remain running so you can perform final development checks like unit and integration tests -
Use
mvn clean verifyto validate that all unit tests and integration tests are passing, and verify code quality and coverage checks are successful
-
Common commands for troubleshooting with Skaffold
Kustomize is what is used to build our final deployment artifacts for Kubernetes.
Each Skaffold "profile" references a specific Kustomize overlay (i.e., directory containing kustomization.yaml), along with
other build/deploy configurations.
However, if you are trying to see what output Skaffold with Kustomize is generating you can use the following command:
skaffold render # renders the default development configIf you are debugging another profile - for instance map-staging-deploy, the command would be:
skaffold render -p map-staging-deploy # renders the 'map-staging-deploy' skaffold.yaml profileNOTE:The additional deployment profiles in skaffold.yaml set the tagPolicy template to use the VERSION environment variable
for its image tag, so any such environment variables not set on your machine will default to an empty string (which translates
to latest in the case of the image tag).
Useful IntelliJ Plugins
Google Cloud Code Plugin
Google has developed the Cloud Code plugin to assist in the development of Kubernetes-based services using Skaffold.
This plugin is the preferred (and most usable) way to work with Skaffold-based projects and so it is highly recommended to configure it for each project.
Since the skaffold.yaml file is based on our conventional templates, the project can be set up in the plugin as an
existing application.
Once configured, builds can be started from the Run menu. The Debug config automatically sets up the deployment and
IDE settings needed to add breakpoints in the source code and have the application suspend when reached (you don’t have to set up
a separate "Remote JVM Debug" configuration).
The Cloud Code plugin provides only skaffold dev and skaffold debug execution so any other Skaffold commands
needed have to be run via the command-line interface.
|
Features of the Cloud Code plugin include:
-
Simple GUI to control most aspects of the Skaffold configuration
-
Automatic syntax-highlighted log tailing of the main service
-
Automatic port forwarding of all deployed services, obviating the need to supply the
--port-forwardargument -
Clickable forwarded URLs/ports list
-
Dynamic Kubernetes deployment status for each service in the deployment
Cloud Code settings to run/debug in Intellij
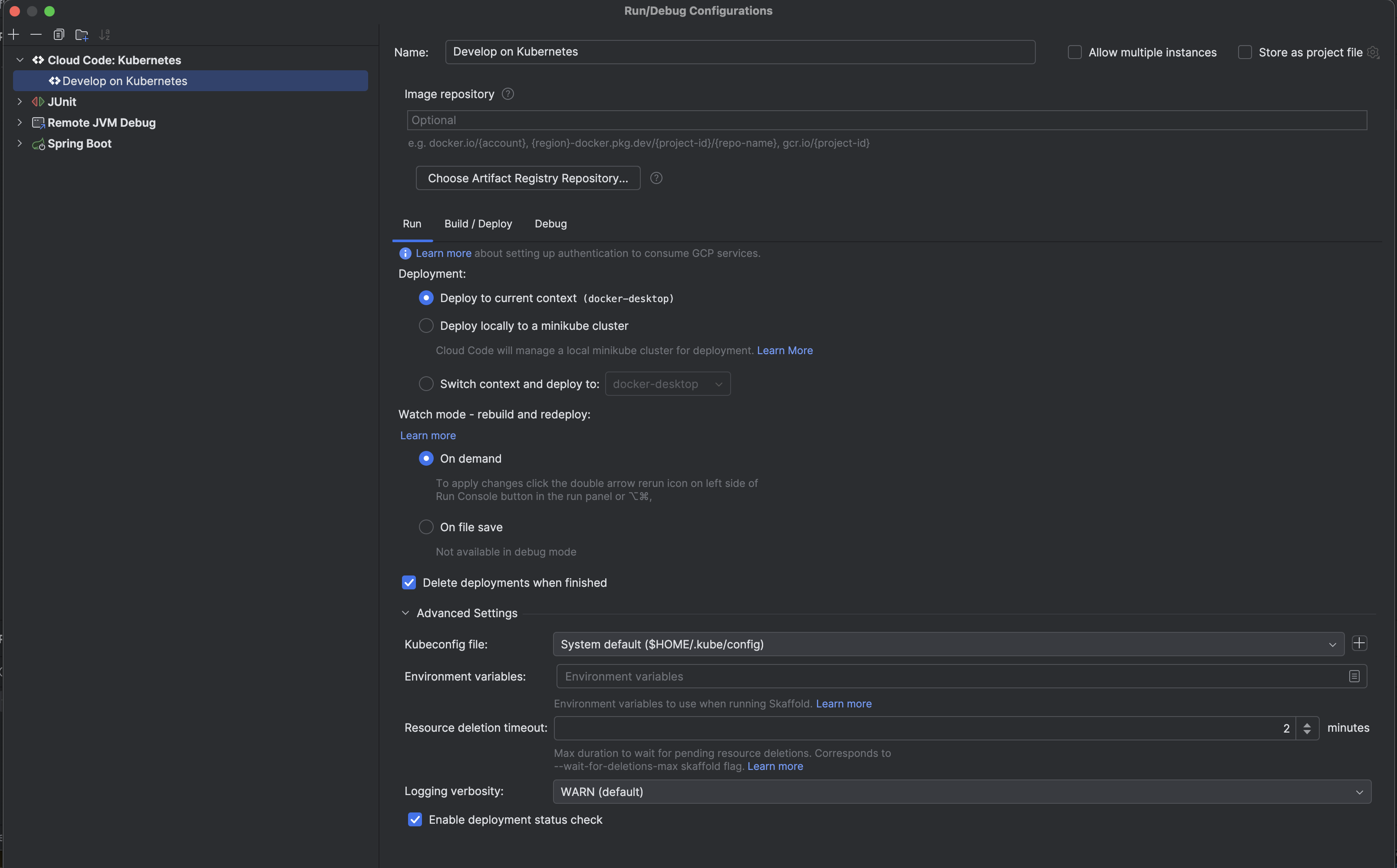
Kubernetes Plugin
Another useful tool in viewing Kubernetes-based deployments is the standard IntelliJ IDEA
Kubernetes Plugin, which is a more generic Kubernetes navigation
and command execution tool that has most of the features as the kubectl CLI, but with an easy-to-use IDE-based UI.
Features of this plugin include:
-
Log tailing any deployment
-
Interactive terminal for containers
-
Built-in
kubectlcommands likedescribe,delete, etc. -
Resource YAML viewer
Having these tools immediately accessible should improve the speed of troubleshooting specific issues so that the necessary changes can be made via additional Kustomize patches.